Solving Variational Problems and Partial Differential Equations that Map between Manifolds via the Closest Point Method
Nathan King and Steven Ruuth
Journal of Computational Physics 2017
Abstract
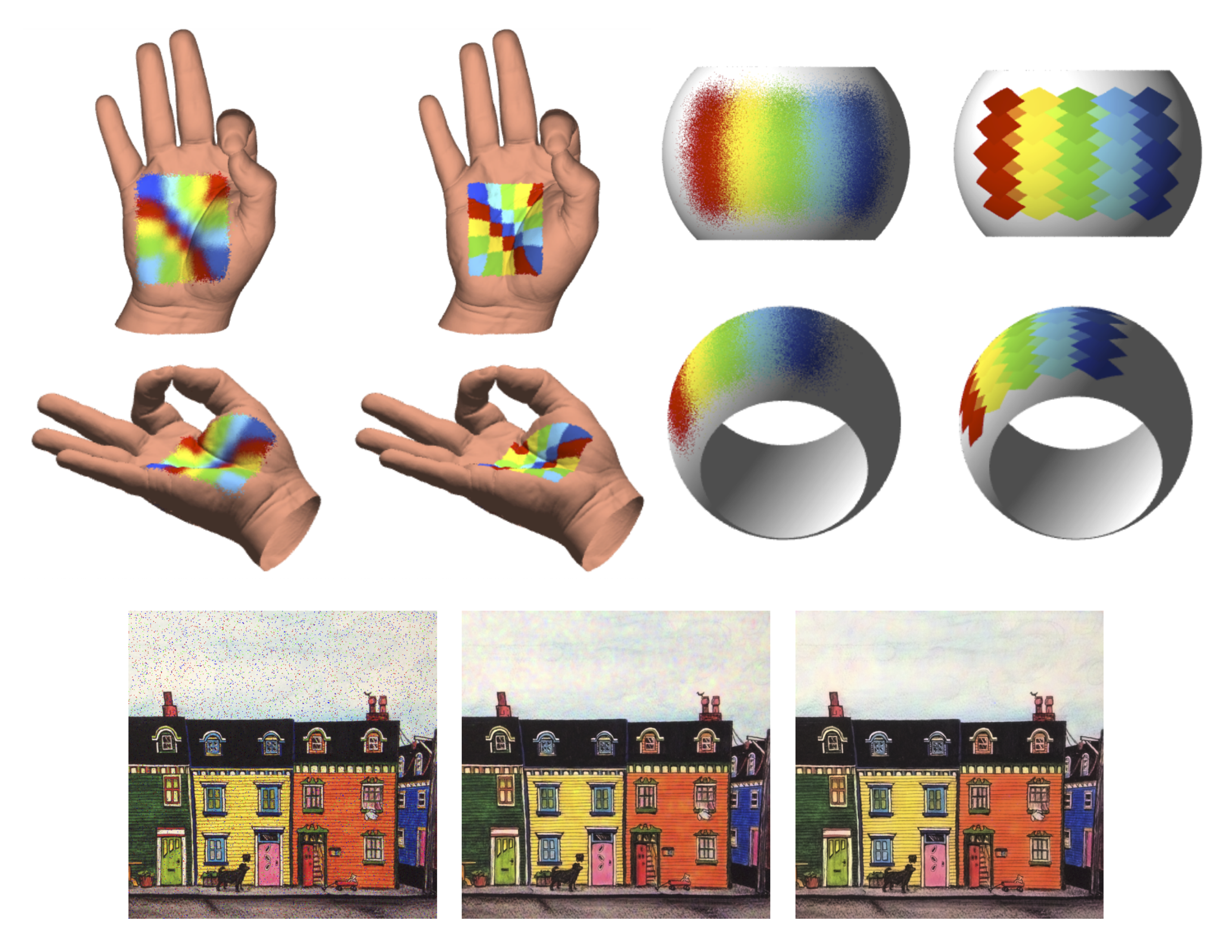
Maps from a source manifold \(\mathcal{M}\) to a target manifold \(\mathcal{N}\) appear in liquid crystals, colour image enhancement, texture mapping, brain mapping, and many other areas. A numerical framework to solve variational problems and partial differential equations (PDEs) that map between manifolds is introduced within this paper. Our approach, the closest point method for manifold mapping, reduces the problem of solving a constrained PDE between manifolds \(\mathcal{M}\) and \(\mathcal{N}\) to the simpler problems of solving a PDE on \(\mathcal{M}\) and projecting to the closest points on \(\mathcal{N}\). In our approach, an embedding PDE is formulated in the embedding space using closest point representations of \(\mathcal{M}\) and \(\mathcal{N}\). This enables the use of standard Cartesian numerics for general manifolds that are open or closed, with or without orientation, and of any codimension. An algorithm is presented for the important example of harmonic maps and generalized to a broader class of PDEs, which includes \(p\)-harmonic maps. Improved efficiency and robustness are observed in convergence studies relative to the level set embedding methods. Harmonic and p-harmonic maps are computed for a variety of numerical examples. In these examples, we denoise texture maps, diffuse random maps between general manifolds, and enhance colour images.
Citation
@article{king2017solving,
title={Solving Variational Problems and Partial Differential Equations that Map between Manifolds via the Closest Point Method},
author={King, Nathan D. and Ruuth, Steven J.},
journal={Journal of Computational Physics},
volume={336},
pages={330--346},
year={2017},
publisher={Elsevier},
doi={https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcp.2017.02.019}
}